Table of contents
- Jenkins Interview Questions For Freshers
- What is Jenkins?
- Tell me something about Continuous Integration, Continuous Delivery, and Continuous Deployment.
- What are the common use cases Jenkins is used for?
- What are the ways to install Jenkins?
- What is a Jenkins job?
- What is a Jenkins Pipeline?
- What are the types of Jenkins pipelines?
- Explain Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline.
- How do you store credentials in Jenkins securely?
- How can we stop a scheduled job from being executed temporarily?
- Intermediate Questions
- What are the ways to trigger a Jenkins Job/Pipeline?
- What is Jenkins Build Cause?
- How does Jenkins know when to execute a Scheduled job/pipeline and how it is triggered?
- What are the credential types supported by Jenkins?
- What are the Scopes of Jenkins Credentials?
- What is the Blue Ocean?
- What is the Jenkins User Content service?
- Advanced Interview Questions
- How is continuous integration achieved using Jenkins?
- How can we share information between different build steps or stages in a Jenkins Job?
- How code coverage is measured/tracked using Jenkins in a CI environment?
- How to do Global Tools Configuration in Jenkins?
- What is Jenkins Remote Access API?
- Can we monitor Jenkins using common Observability tools?
- What is a Ping Thread in Jenkins and how it works?
- Conclusion
Jenkins Interview Questions For Freshers
What is Jenkins?
Jenkins is a self-contained, open-source automation server that can be used to automate all sorts of tasks related to building, testing and delivering or deploying software. Jenkins can be installed through native system packages, Docker, or even run standalone by any machine with a Java Runtime Environment (JRE) installed.
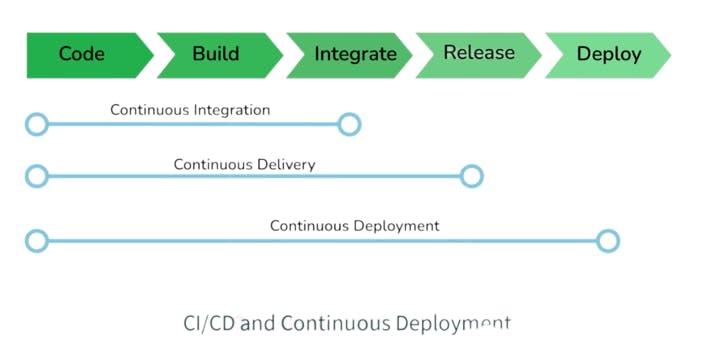
Tell me something about Continuous Integration, Continuous Delivery, and Continuous Deployment.
Continuous Integration: A software development process where the changes made to software are integrated into the main code as and when a patch is ready so that the software will be always ready to be - built, tested, deployed, and monitored - continuously.
Continuous Delivery: This is a Software Development Process where the continuously integrated (CI) changes will be tested & deployed continuously into a specific environment, generally through a manual release process, after all the quality checks are successful.
Continuous Deployment: A Software Development practice where the continuously integrated (CI) changes are deployed automatically into the target environment after all the quality checks are successful.
What are the common use cases Jenkins is used for?
Jenkins being open-source automation can be used for any kind of software-based automation. Some of the common use cases include but are not limited to -
Software build jobs
Sanity/Smoke/CI/Regression test jobs
Web/Data Scraping related jobs
Code coverage measurement jobs
General-purpose automation
Reverse Engineering jobs
Key Decoding jobs & many other jobs where software automation will be
applicable.
What are the ways to install Jenkins?
Jenkins can be installed using:
Native System Package Manager like - apt (Linux), brew (Mac), etc.
Docker (popular docker images for Jenkins is available for different platforms like Unix/Mac/Windows in the docker registry).
Kubernetes (available as a helm chart and can be installed on our Kubernetes clusters).
Standalone (on any machine with a Java Runtime Environment installed)
For more detailed installation instructions refer to the official documentation
What is a Jenkins job?
A Job/Project is the fundamental unit of a logical work (like a software build, an automation task, test execution, etc) using the Jenkins automation server and other required plugins, configurations & infrastructures. Jobs can be of different types like - a freestyle project, a multi-configuration project, a pipeline project, a multi-branch project, etc.
What is a Jenkins Pipeline?
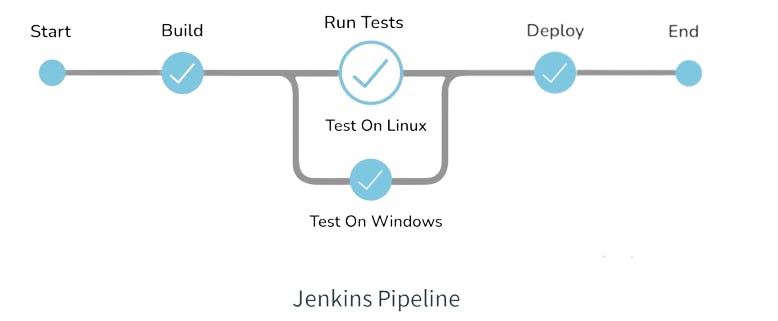
The pipeline is a special type of Jenkins job - simply a sequence of steps controlled by a defined logic - which Orchestrates long-running activities that can span across multiple build agents. It is suitable for building pipelines (formerly known as workflows) and/or organizing complex activities that cannot be easily achieved using a freestyle job.
What are the types of Jenkins pipelines?
Jenkins Pipelines can be either - A declarative pipeline or a Scripted Pipeline. Declarative pipeline makes use of numerous, generic, predefined build steps/stages (i.e. code snippets) to build our job according to our build/automation needs whereas, with Scripted pipelines, the steps/stages can be custom-defined & used using a groovy syntax which provides better control & fine-tuned execution levels.
Explain Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline.
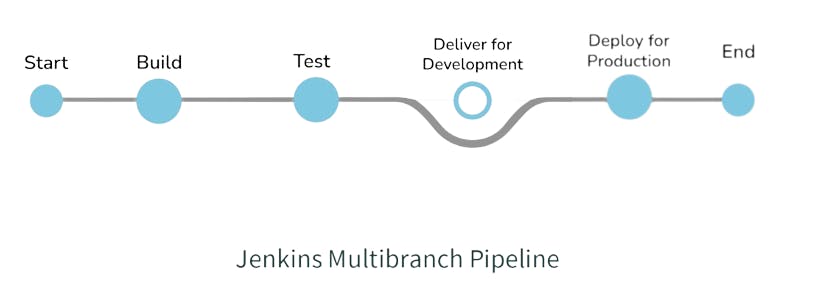
It is a pipeline job that can be configured to Create a set of Pipeline projects according to the detected branches in one SCM repository. This can be used to configure pipelines for all branches of a single repository e.g. if we maintain different branches (i.e. production code branches) for different configurations like locales, currencies, countries, etc.
How do you store credentials in Jenkins securely?
Credentials can be stored securely in Jenkins using the Credentials plugin, which stores different types of credentials like - Username with a password, SSH username with the private key, AWS Credentials, Jenkins Build Token, Secret File/Text, X509 & other certificates, Vault related credentials securely with proper encryption & decryption as and when required.
How can we stop a scheduled job from being executed temporarily?
Disable the job from the job details page to temporarily stop all scheduled executions & other factors/events from triggering the job and enable it back to resume the job schedules/triggers. If a job is not required permanently, we can delete the job from the jobs list view page.
Intermediate Questions
What are the ways to trigger a Jenkins Job/Pipeline?
There are many ways we can trigger a job in Jenkins:
Trigger an API (POST) request to the target job URL with the required data.
Trigger it manually from the Jenkins web application.
Trigger it using Jenkins CLI from the master/slave nodes.
Time-based Scheduled Triggers like a cron job.
Event-based Triggers like SCM Actions (Git Commit, Pull Requests), WebHooks, etc.
Upstream/Downstream triggers by other Jenkins jobs.
What is Jenkins Build Cause?
Build Cause is a text attribute that represents what made a job's build be triggered, say it could be a Jenkins User (from UI), Timer for Scheduled jobs, Upstream jobs for a job which was triggered by an upstream job, etc. This is mainly used to identify the nature of the builds - be it nightly, manual, automated, etc.
How does Jenkins know when to execute a Scheduled job/pipeline and how it is triggered?
The Jenkins master will have the cron entries set up for the jobs as per the scheduled job configurations. As and when the time for a particular job comes, it commands agents (based on the configuration of the job) to execute the job with the required configurations.
What are the credential types supported by Jenkins?
In Jenkins, credentials are a set of information used for authentication with internal/external services to accomplish an action. Jenkins credentials are provisioned & managed by a built-in plugin called - The credentials Binding - plugin. Jenkins can handle different credentials as follows:
Secret text - A token such as an API token, JSON token, etc.
Username and password - Basic Authentication can be stored as a credential as well.
Secret file - A secret file used to authenticate some secure data services & security handshakes.
SSH Username with a private key - An SSH public/private key pair for Machine to Machine authentication.
Certificate - a PKCS#12 certificate file and an optional password.
Docker Host Certificate Authentication credentials.
And as we can guess, this can be extended to several other extensible credential types like - AWS credentials, Azure secrets, etc. using commonly available plugins.
What are the Scopes of Jenkins Credentials?
Jenkins credentials can be of one of the two scopes - Global & System
Global - the credential will be usable across all the jobs configured in the Jenkins instance (i.e. for all jobs). This is more suited for user Jobs (i.e. for the freestyle, pipeline, or other jobs) to authenticate itself with target services/infrastructures to accomplish the purpose of the job)
System - This is a special scope that will allow Jenkins itself (i.e. the core Jenkins functionalities & some installed plugins) to authenticate itself to external services/infrastructures to perform some defined tasks. E.g. sending emails, etc.
What is the Blue Ocean?
Blue Ocean is the redefined user experience for Jenkins. Designed from the ground up for Jenkins Pipeline, it is still compatible with freestyle jobs, Blue Ocean reduces clutter and increases clarity. Blue Ocean’s main features include -:
Sophisticated visualizations of continuous delivery (CD) Pipelines, allowing for fast and intuitive comprehension of your Pipeline’s status.
Pipeline editor - makes the creation of Pipelines approachable by guiding the user through an intuitive and visual process to create a Pipeline.
Personalization to suit the role-based needs of each member of the team.
Pinpoint precision when intervention is needed and/or issues arise. Blue Ocean shows where in the pipeline attention is needed, facilitating exception handling and increasing productivity.
Native integration for branch and pull requests, enables maximum developer productivity when collaborating on code with others in GitHub, Bitbucket, etc.
What is the Jenkins User Content service?
Jenkins has a mechanism known as "User Content", where administrators can place files inside the $JENKINS_HOME/userContent folder and these files are served from yourhost/jenkins/userContent.
This can be thought of as a mini HTTP server to serve images, stylesheets, and other static resources that you can use from various description fields inside Jenkins.
Advanced Interview Questions
How is continuous integration achieved using Jenkins?
Continuous integration is a process where a developer’s code changes are constantly integrated into the main code and the same will be tested automatically the results of the tests will decide whether the change is ready for deployment. In this process -:
Developer Makes a change - commit/pull_request - in the feature/dev branch
Source Control Management system generates appropriate events
SCM Specific Jenkins Plugins like Git/SVN will detect those events from the configured repositories and these events will be used to Trigger - build/dependent/test - jobs on Jenkins
After the Test/Dependent jobs are completed, the change/patch will be labeled according to the status of the test job
Based on the Status (i.e. readiness of a change to be merged with the main branch), the Continuous Delivery or Continuous Deployment strategy/tool will take it forward.
How can we share information between different build steps or stages in a Jenkins Job?
Every build step or stage will be running in its process and hence sharing information between two different build steps is not so direct. We can use either a File, a Database Entry, an Environment Variable, etc. to share info from one build step to another or a post-build action.
How code coverage is measured/tracked using Jenkins in a CI environment?
Using language-specific code coverage plugins like JaCoCo, CodeCov, etc or generic tools/plugins like Sonarqube which will add the code coverage data to builds with some minor tweaks in the code and the same can be displayed as a graph in Jenkins.
How to do Global Tools Configuration in Jenkins?
Global Tools are tools that need to be installed outside the Jenkins environment and need to be controlled from within the Jenkins environment. Hence it needs its corresponding Jenkins plugin as well. Steps to using a Global Tool generally include:
Install the tool Plugin into the Jenkins instance, to include the global tool in a list of global tools used by Jenkins.
Install the tool in the Jenkins instance or provide a way (maybe a command to download and) install the tool during runtime.
Go to Manage Jenkins -> Global Tools Configuration Scroll through the tool list and configure the global tool-specific configurations.
Make use of the installed global Tool in your job/pipeline.
What is Jenkins Remote Access API?
Jenkins provides remote access API to most of its functionalities (though some functionalities are programming language-dependent). Currently, it comes in three flavors -:
XML
JSON with JSONP support
Python
Remote access API is offered in a REST-like style. That is, there is no single entry point for all features, instead, they are available under the ".../API/" URL where the "..." portion is the data that it acts on.
For example, if your Jenkins installation sits at makemytrip.com, visiting /API/ will show just the top-level API features available – primarily a listing of the configured jobs for this Jenkins instance.
Or if we want to access information about a particular build, e.g. ci.jenkins.io/job/Infra/job/jenkins.io/job/.., then go to ci.jenkins.io/job/Infra/job/jenkins.io/job/.. and you’ll see the list of functionalities for that build.
Can we monitor Jenkins using common Observability tools?
Common monitoring platforms like DataDog, Prometheus, JavaMelody & few others - have their corresponding Jenkins plugin, which when configured, sends Metrics to the corresponding Monitoring platform, which can then be Observed with the latest tools & technologies. The same can be configured with Alarms & Notifications for immediate attention when something goes wrong.
What is a Ping Thread in Jenkins and how it works?
Jenkins installs a "ping thread" on every remote connection, such as Controller/Agent connections, regardless of its transport mechanism (such as SSH, JNLP, etc.). The lower level of the Jenkins Remoting Protocol is a message-oriented protocol, and a ping thread periodically sends a ping message that the receiving end will reply to. The ping thread measures the time it takes for the reply to arrive, and if it’s taking excessive time (currently 4 minutes and configurable), then it assumes that the connection was lost and initiates the formal close down.
This is to avoid an infinite hang, as some of the failure modes in the network cannot be detected otherwise. The timeout is also set to a long enough value so that a temporary surge in the load or a long garbage collection pause will not trip off the close-down.
Ping thread is installed on both controller & agent; each side pings the other and tries to detect the problem from their side.
The ping thread time out is reported through java.util.logging. Besides, the controller will also report this exception in the agent launch log. Note that some agent launchers, most notably SSH agents, writes all stdout/stderr outputs from the agent JVM into this same log file, so you need to be careful.
Conclusion
Though these are not the complete possibilities of Jenkins, i tried to cover some of the commonly asked interview questions on core Jenkins. We also need to understand that the Jenkins Update Center is enriched with thousands of useful plugins that enhance the supported functionalities of Jenkins.
Also, try creating a pipeline project with JenkinsFile and a global shared Jenkins library and build the job successfully. This will help us learn how Jenkins works with some hands-on issues.