Dockerize Python App
Create Jenkins Pipeline for automating Docker image creation and push docker image into Docker Hub
Context
We will learn how to automate Docker builds using Jenkins. We will use a Python-based application. I have already created a repo with source code + Dockerfile. We will be creating a Declarative Jenkins pipeline for automating builds.
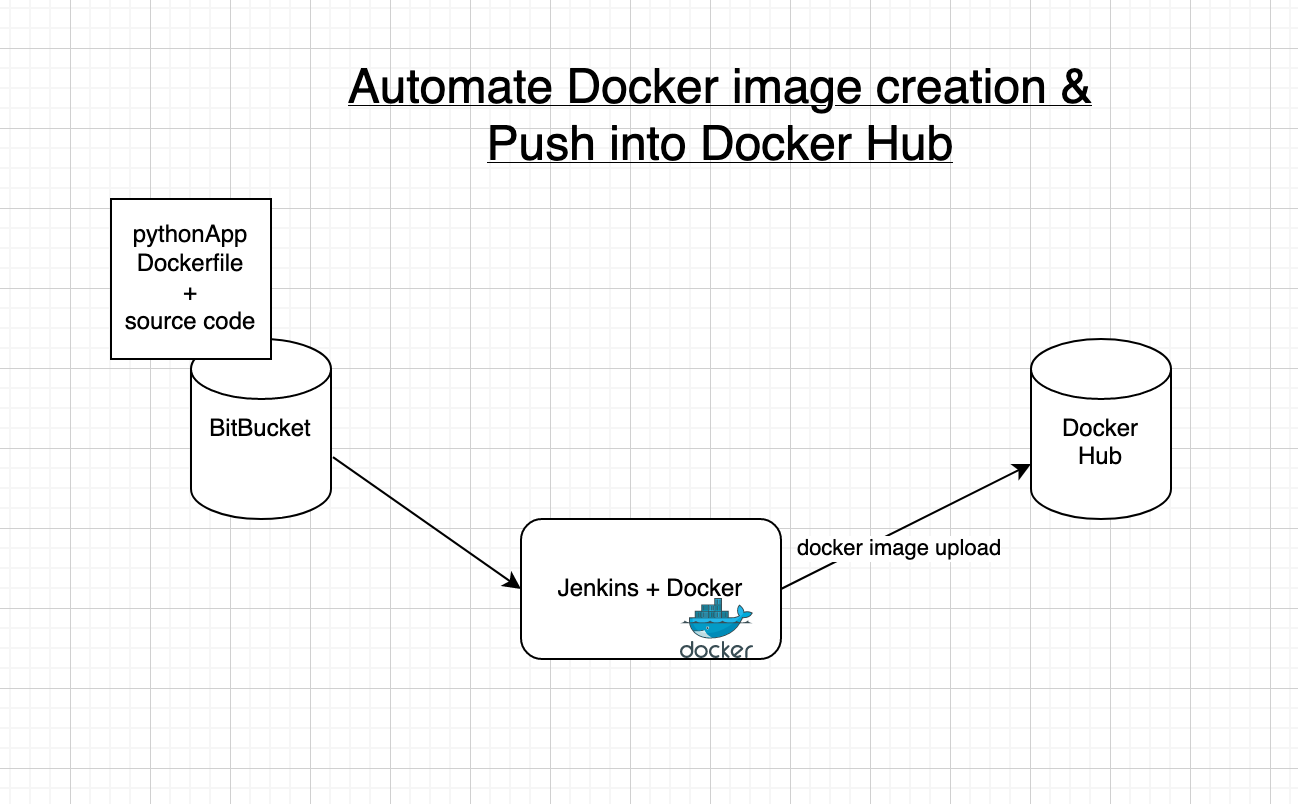
- Automating builds.
- Automating Docker image creation.
- Automating Docker image upload.
- Automating Docker container provisioning.
Pre-requisites:
1. Jenkins is up and running
2. Docker installed on Jenkins instance and configured.
3. Docker plug-in installed in Jenkins
4. user account setup in cloud.docker.com
5. port 8096 is opened up in firewall rules.

Let's Start with Jenkins
Step #1 - Create Credentials for Docker Hub
Go to your Jenkins where you have installed Docker as well. Go to credentials -->
Click on Global credentials
Click on Add Credentials
Now Create an entry for Docker Hub credentials

Make sure you take note of the ID as circled below:

Step # 2 - Create a Jenkins pipeline

Step # 3 - Write the pipeline code
Make sure you change the Emoji highlighted values below:
Your docker user id should be updated.
your registry credentials ID from Jenkins from step # 1 should be copied.
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
//once you sign up for Docker hub, use that user_id here
registry = "your_docker_user_id✍️/mypythonapp"
//- update your credentials ID after creating credentials for connecting to Docker Hub
registryCredential = 'fa32f95a-2d3e-4c7b-8f34-11bcc0191d70✍️'
//use your own dockercredential ID
}
stages {
stage('Cloning Git') {
steps {
checkout([$class: 'GitSCM', branches: [[name: '*/master']], doGenerateSubmoduleConfigurations: false, extensions: [], submoduleCfg: [], userRemoteConfigs: [[credentialsId: '', url: 'https://bitbucket.org/biswajitmoahapatra/mypythonrepo']]])
}
}
// Building Docker images
stage('Building image') {
steps{
script {
dockerImage = docker.build registry
}
}
}
// Uploading Docker images into Docker Hub
stage('Upload Image') {
steps{
script {
docker.withRegistry( '', registryCredential ) {
dockerImage.push()
}
}
}
}
// Stopping Docker containers for cleaner Docker run
stage('docker stop container') {
steps {
sh 'docker ps -f name=mypythonappContainer -q | xargs --no-run-if-empty docker container stop'
sh 'docker container ls -a -fname=mypythonappContainer -q | xargs -r docker container rm'
}
}
// Running Docker container, make sure port 8096 is opened in Your VM
stage('Docker Run') {
steps{
script {
dockerImage.run("-p 8096:5000 --rm --name mypythonappContainer")
}
}
}
}
}
Step # 4 - Click on Build - Build the pipeline
Once you create the pipeline and change values per your Docker user id and credentials ID, click on Save and Apply. Then Click Build Option.
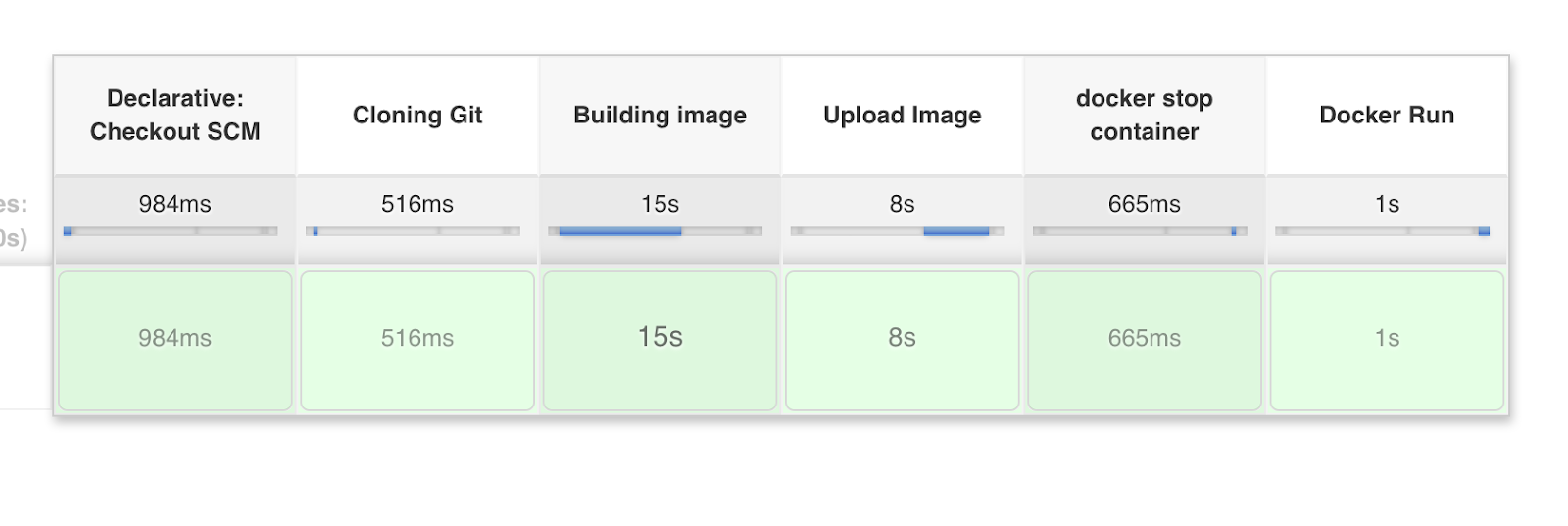
Step # 5 - Access Python App
Once the build is successful, go to the browser and enter public_dns_name:8096
You should see the page like below:

Conclusion
Congratulations you successfully completed your first project.
Your Pipelining Project is done🤟🤟...
Enjoy!!
If you liked this blog post, consider liking and commenting on it and Sharing it with your friends.
~Biswajit Mohapatra