Table of contents
- AWS Basic Interview Questions
- 1. What is AWS?
- 2. What is EC2?
- 3. What is SnowBall?
- 4. What is CloudWatch?
- 5. What do you understand by VPC?
- 6. DNS and Load Balancer Services come under which type of Cloud Service?
- 7. What are the Storage Classes available in Amazon S3?
- 8. What are Key-Pairs in AWS?
- 9. How many Subnets can you have per VPC?
- 10. List different types of Cloud Services.
- Advanced AWS Questions
- 1. Explain what S3 is?
- 2. How does Amazon Route 53 provide high availability and low latency?
- 3. How can you send a request to Amazon S3?
- 4. What does AMI include?
- 5. What are the different types of Instances?
- 6. What is the relation between the Availability Zone and Region?
- 7. How do you monitor Amazon VPC?
- 8. What are the advantages of AWS IAM?
- 9. What do you understand by a Security Group?
- 10. What are Spot Instances and On-Demand Instances?
- 11. What is a Stateful and a Stateless Firewall?
- 12. What is an Instance Store Volume and an EBS Volume?
- 13. Can you change the Private IP Address of an EC2 instance while it is running or in a stopped state?
- 14. What is the use of lifecycle hooks in Autoscaling?
- 15. What are the policies that you can set for your user’s passwords?
- 16. What are the different types of EC2 instances based on their costs?
AWS Basic Interview Questions
1. What is AWS?
AWS is a cloud computing service offered by Amazon. AWS lets you build, test, deploy and manage applications and services. All this is done via the data centers and the hardware managed by Amazon. AWS provides you with a combination of Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Soware-as-a-Service (SaaS) offerings.
You can use AWS to create Virtual Machines which can be armed with processing power, storage capacity, and analytics along with networking and device management. AWS offers you a pay-as-you-go model, which helps to avoid upfront costs and pay based on usage monthly.
2. What is EC2?
EC2 stands for Elastic Compute Cloud. EC2 is a Virtual Machine in the cloud on which you have OS-level control. You can run this cloud server whenever you want and can be used when you need to deploy your own servers in the cloud, similar to your on-premises servers, and when you want to have full control over the choice of hardware and the updates on the machine.
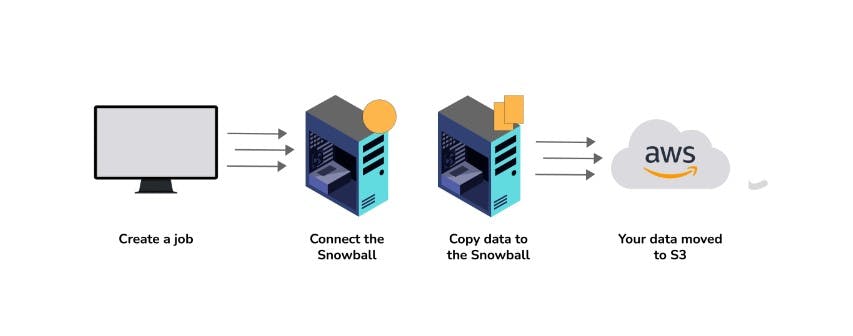
3. What is SnowBall?
SnowBall is a small application that enables you to transfer terabytes of data inside and outside of the AWS environment.
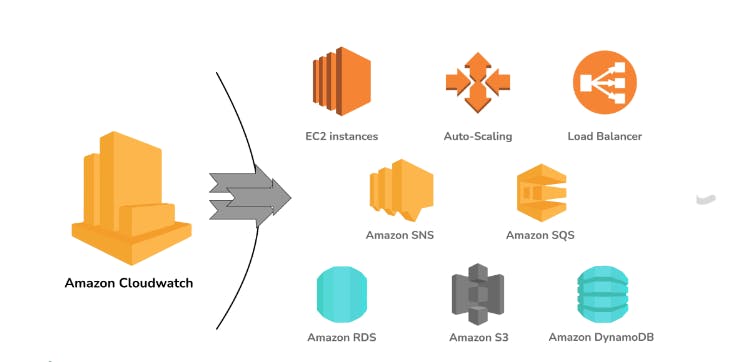
4. What is CloudWatch?
CloudWatch helps you to monitor AWS environments like EC2, RDS Instances, and CPU utilization. It also triggers alarms depending on various metrics.
5. What do you understand by VPC?
VPC stands for Virtual Private Cloud. It allows you to customize your networking configuration. VPC is a network that is logically isolated from other networks in the cloud. It allows you to have your private IP Address range, internet gateways, subnets, and security groups.
6. DNS and Load Balancer Services come under which type of Cloud Service?
DNS and Load Balancer are a part of IaaS-Storage Cloud Service.
7. What are the Storage Classes available in Amazon S3?
Storage Classes available with Amazon S3 are:
Amazon S3 Standard
Amazon S3 Standard-Infrequent Access
Amazon S3 Reduced Redundancy Storage
Amazon Glacier
8. What are Key-Pairs in AWS?
Key-Pairs are secure login information for your Virtual Machines. To connect to the instances, you can use Key-Pairs which contain a Public Key and a Private Key.
9. How many Subnets can you have per VPC?
You can have 200 Subnets per VPC.
10. List different types of Cloud Services.
Different types of Cloud Services are:
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Data as a Service (DaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Advanced AWS Questions
1. Explain what S3 is?
S3 stands for Simple Storage Service. You can use the S3 interface to store and retrieve any amount of data, at any time and from anywhere on the web. For S3, the payment model is “pay as you go”.
2. How does Amazon Route 53 provide high availability and low latency?
Globally Distributed Servers - Amazon is a global service and consequently has DNS Servers globally. Any customer creating a query from any part of the world gets to reach a DNS Server local to them that provides low latency.
Dependency - Route 53 provides a high level of dependability required by critical applications.
Optimal Locations - Route 53 serves the requests from the nearest data center to the client sending the request. AWS has data centers across the world. The data can be cached in different data centers located in different regions of the world depending on the requirements and the configuration chosen. Route 53 enables any server in any data center which has the required data to respond. This way, it enables the nearest server to serve the client request, thus reducing the time taken to serve.
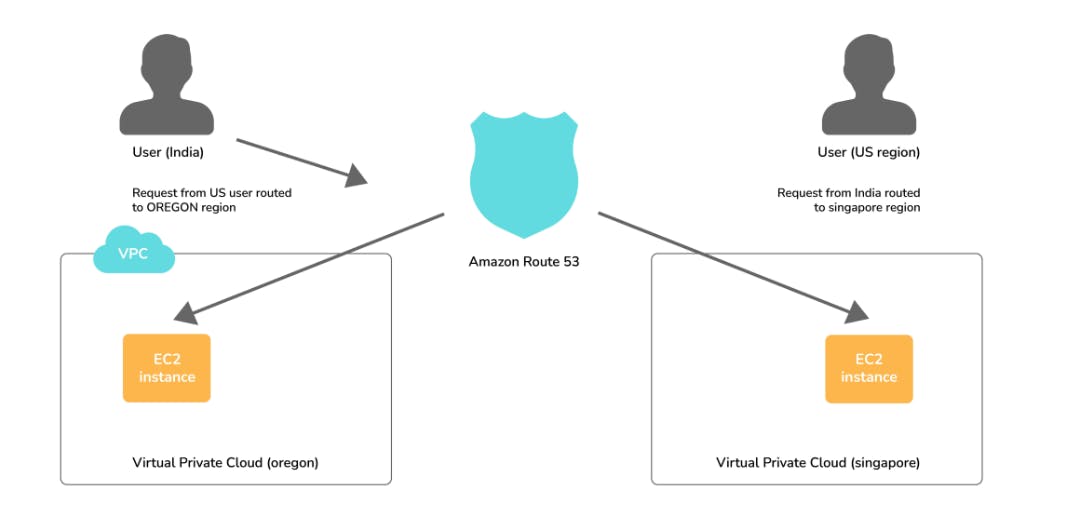
As can be seen in the above image, the requests coming from a user in India are served from the Singapore Server, while the requests coming from a user in the US are routed to the Oregon region.
3. How can you send a request to Amazon S3?
Amazon S3 is a REST Service, and you can send a request by using the REST API or the AWS SDK wrapper libraries that wrap the underlying Amazon S3 REST API.
4. What does AMI include?
An AMI includes the following things:
A template for the root volume for the instance.
Launch permissions to decide which AWS accounts can avail the AMI to launch instances.
A block device mapping that determines the volumes to attach to the instance when it is launched.
5. What are the different types of Instances?
Compute Optimized
Memory-Optimized
Storage Optimized
Accelerated Computing
General Purpose
6. What is the relation between the Availability Zone and Region?
An AWS Availability Zone is a physical location where an Amazon data center is located. On the other hand, an AWS Region is a collection or group of Availability Zones or Data Centers.
This setup helps your services to be more available as you can place your VMs in different data centers within an AWS Region. If one of the data centers fails in a Region, the client requests still get served from the other data centers located in the same Region. This arrangement, thus, helps your service to be available even if a Data Center goes down.
7. How do you monitor Amazon VPC?
CloudWatch
VPC Flow Logs
8. What are the advantages of AWS IAM?
AWS IAM enables an administrator to provide granular-level access to different users and groups. Different users and user groups may need different levels of access to different resources created. With IAM, you can create roles with specific access levels and assign the roles to the users.
It also allows you to provide access to the resources to users and applications without creating the IAM Roles, which is known as Federated Access.
9. What do you understand by a Security Group?
When you create an instance in AWS, you may or may not want that instance to be accessible from the public network. Moreover, you may want that instance to be accessible from some networks and not from others.
Security Groups are a type of rule-based Virtual Firewall using which you can control access to your instances. You can create rules defining the Port Numbers, Networks, or protocols from which you want to allow access or deny access.
10. What are Spot Instances and On-Demand Instances?
When AWS creates EC2 instances, there are some blocks of computing capacity and processing power left unused. AWS releases these blocks as Spot Instances. Spot Instances run whenever capacity is available. These are good options if you are flexible about when your applications can run and if your applications can be interrupted.
On the other hand, On-Demand Instances can be created as and when needed. The prices of such instances are static. Such instances will always be available unless you explicitly terminate them.
11. What is a Stateful and a Stateless Firewall?
A Stateful Firewall maintains the state of the rules defined. It requires you to define only inbound rules. Based on the inbound rules defined, it automatically allows the outbound traffic to flow.
On the other hand, a Stateless Firewall requires you to explicitly define rules for inbound as well as outbound traffic.
For example, if you allow inbound traffic from Port 80, a Stateful Firewall will allow outbound traffic to Port 80, but a Stateless Firewall will not do so.
12. What is an Instance Store Volume and an EBS Volume?
An Instance Store Volume is temporary storage that is used to store the temporary data required by an instance to function. The data is available as long as the instance is running. As soon as the instance is turned off, the Instance Store Volume gets removed and the data gets deleted.
On the other hand, an EBS Volume represents a persistent storage disk. The data stored in an EBS Volume will be available even after the instance is turned off.
13. Can you change the Private IP Address of an EC2 instance while it is running or in a stopped state?
No, a Private IP Address of an EC2 instance cannot be changed. When an EC2 instance is launched, a private IP Address is assigned to that instance at the boot time. This private IP Address is attached to the instance for its entire lifetime and can never be changed.
14. What is the use of lifecycle hooks in Autoscaling?
Lifecycle hooks are used for Auto-scaling to put an additional wait time to a scale-in or a scale-out event.
15. What are the policies that you can set for your user’s passwords?
Following are the policies that can be set for user’s passwords:
You can set a minimum length of the password.
You can ask the users to add at least one number or special character to the password.
Assigning the requirements of particular character types, including uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and non-alphanumeric characters.
You can enforce automatic password expiration, prevent the reuse of old passwords, and request a password reset upon their next AWS sign-in.
You can have the AWS users contact an account administrator when the user has allowed the password to expire.
16. What are the different types of EC2 instances based on their costs?
The three types of EC2 instances based on the costs are:
On-Demand Instance - These instances are prepared as and when needed. Whenever you feel the need for a new EC2 instance, you can go ahead and create an on-demand instance. It is cheap for the short time but not when taken for the long term.
Spot Instance - These types of instances can be bought through the bidding model. These are comparatively cheaper than On-Demand Instances.
Reserved Instance - On AWS, you can create instances that you can reserve for a year or so. These types of instances are especially useful when you know in advance that you will be needing an instance for the long term. In such cases, you can create a reserved instance and save heavily on costs.